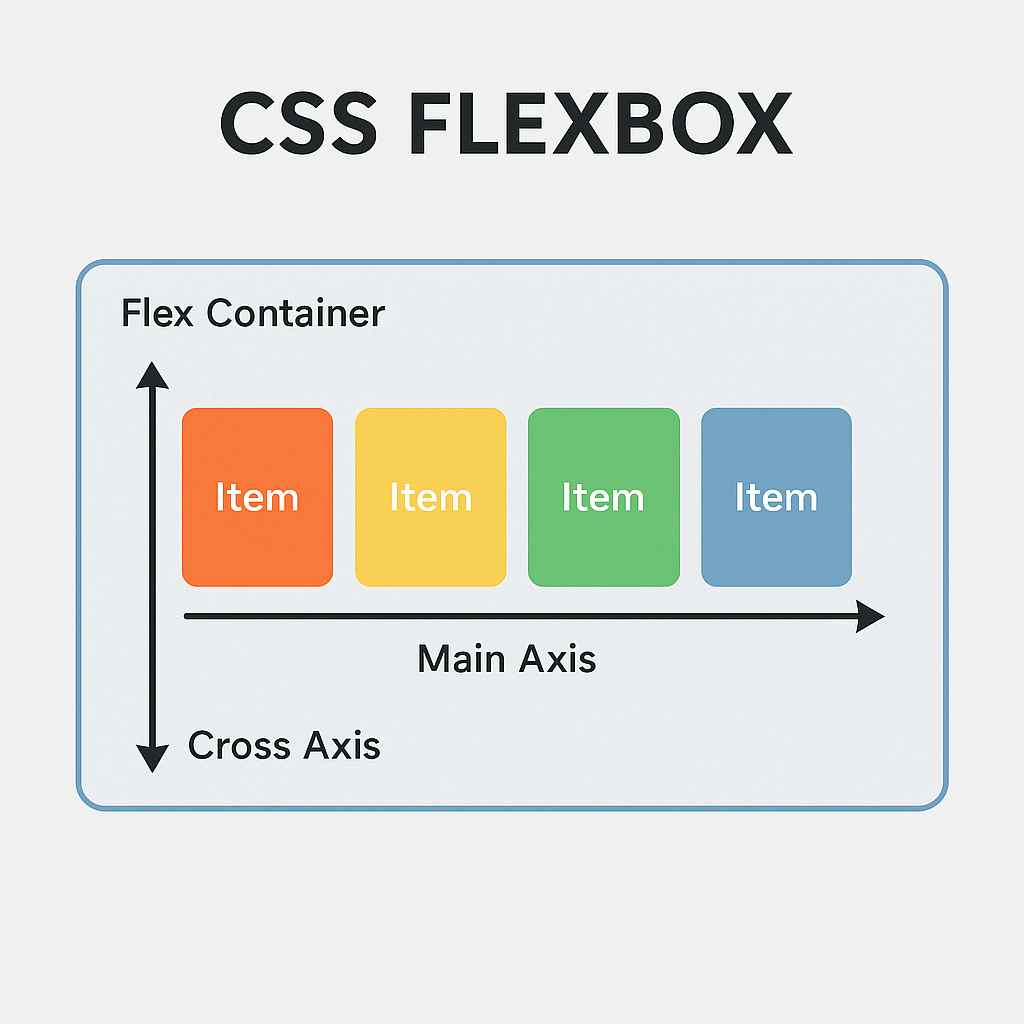
Flexbox (Flexible Box Layout) is a one-dimensional CSS layout system that arranges items horizontally (row) or vertically (column) and adapts them to available space. It’s perfect for dynamic, content-driven designs.
Basic Flexbox Setup
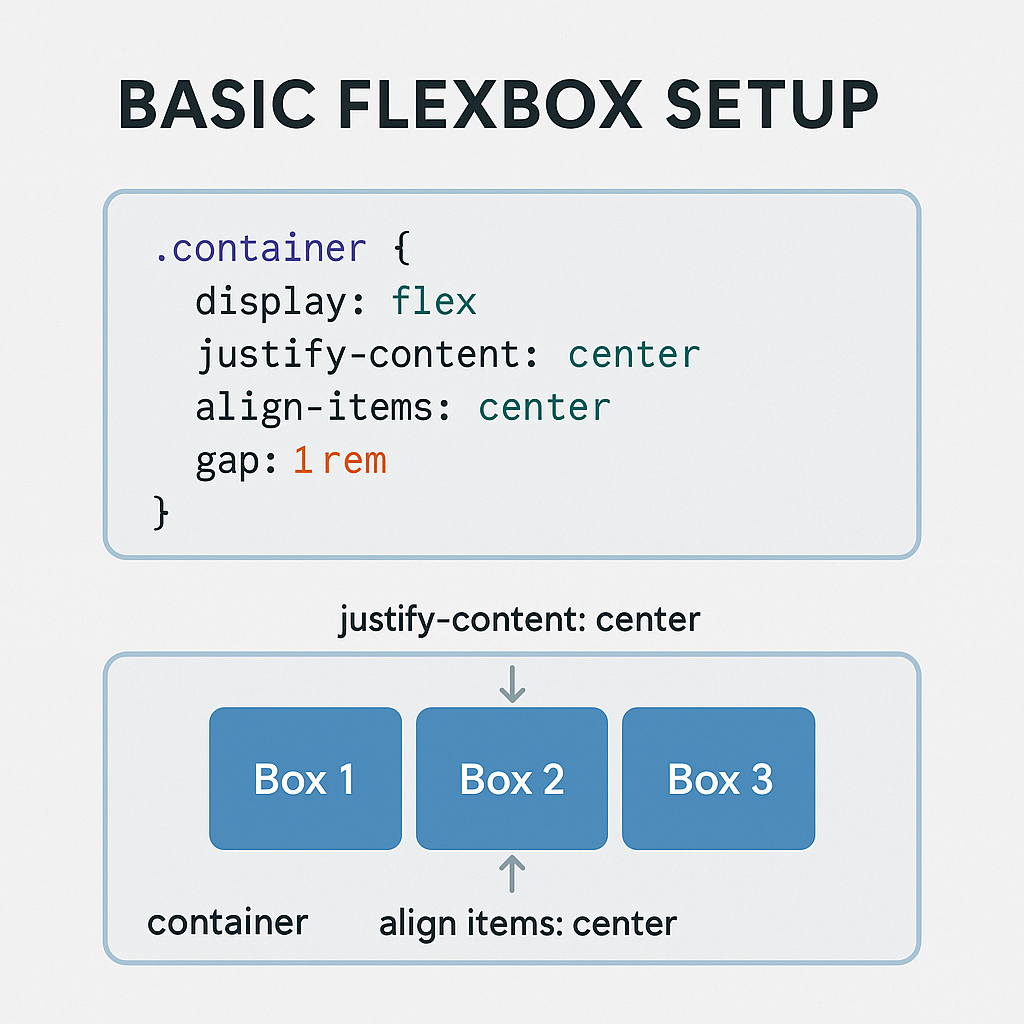
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center; /* Align items along the main axis */
align-items: center; /* Align items along the cross axis */
gap: 1rem; /* Modern spacing between items */
}
<div class="container">
<div class="box">Box 1</div>
<div class="box">Box 2</div>
<div class="box">Box 3</div>
</div>
.box {
background: #4f46e5;
color: white;
padding: 1rem 2rem;
border-radius: 10px;
}
Main Flexbox Properties
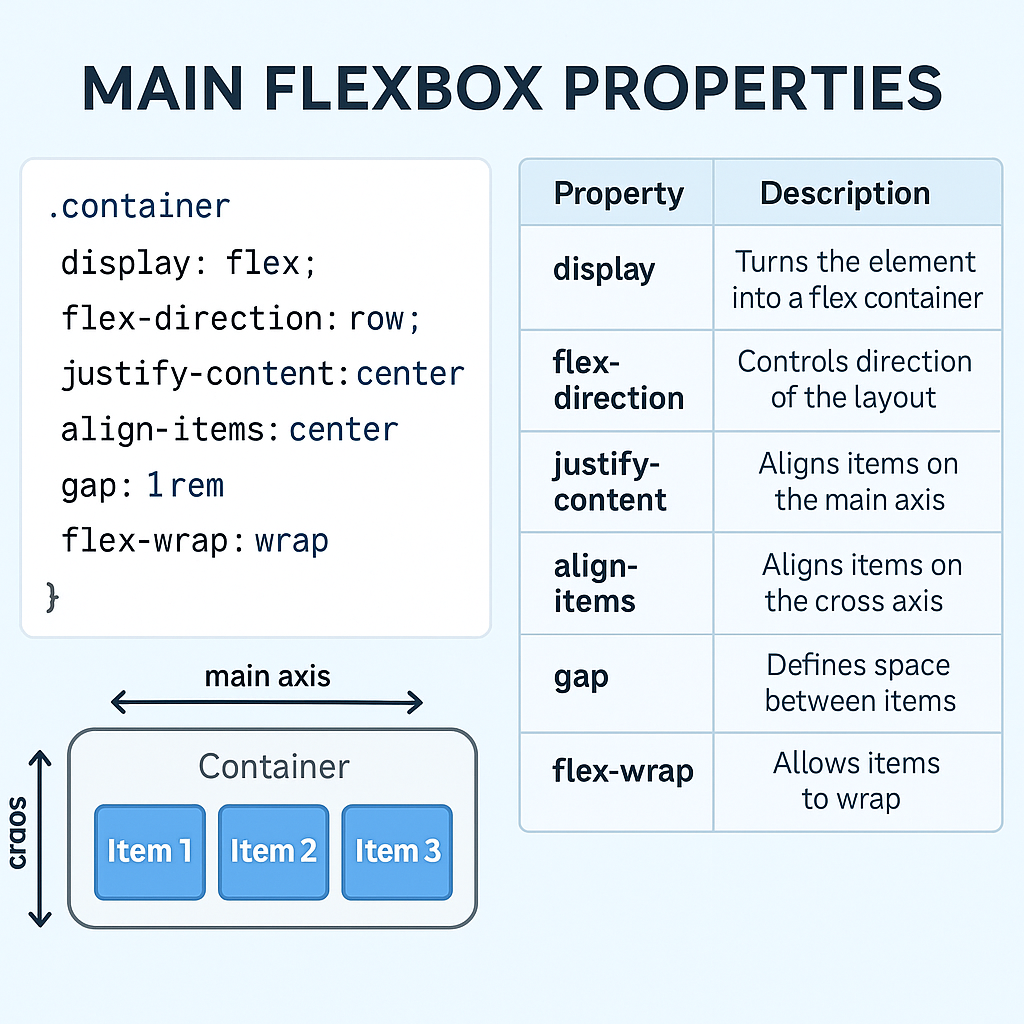
| Property | Purpose |
|---|---|
display: flex | Turns the element into a flex container |
flex-direction | Direction of layout: row, column |
justify-content | Aligns items on the main axis |
align-items | Aligns items on the cross axis |
gap | Adds space between flex items (modern!) |
flex-wrap | Allows wrapping (wrap, nowrap) |
flex | Defines grow, shrink, and basis |
Responsive Flexbox Layout
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-between;
gap: 1rem;
}
.item {
flex: 1 1 250px; /* Grow/shrink/basis */
}
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Item A</div>
<div class="item">Item B</div>
<div class="item">Item C</div>
</div>
Centering Techniques
Center an element both horizontally and vertically:
.center {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
}
Modern Best Practices (2025)
Use gap instead of margins
.container {
display: flex;
gap: 1rem; /* Cleaner than using margin */
}
Use logical properties for direction
flex-direction: row; /* Left-to-right layout */
flex-direction: column; /* Top-to-bottom layout */
Use min-width or flex-basis for flexible items
.item {
flex: 1 1 200px;
}
Combine Flexbox + Media Queries for responsiveness
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.container {
flex-direction: column;
}
}
Latest Flexbox Trends (2025)
- Use
gapfor spacing (supported in all major browsers). - Component-level Flexbox: Use inside cards, navbars, modals.
- Use utility-first CSS (e.g., Tailwind CSS) for rapid flex layout prototyping.
- Mix with CSS Grid for complex page layouts.
- Container Queries (experimental but gaining support) for layout responsiveness.
Real World Example: Flex Navbar
<nav class="navbar">
<div class="logo">MySite</div>
<div class="nav-links">
<a href="#">Home</a>
<a href="#">About</a>
<a href="#">Contact</a>
</div>
</nav>
.navbar {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
padding: 1rem 2rem;
background: #111827;
color: white;
}
.nav-links {
display: flex;
gap: 1.5rem;
}
Summary: When to Use Flexbox
Great For:
- Centering content
- Navigation bars
- Aligning icons/text
- Button groups
- Wrapping row/column content
Avoid Flexbox When:
- You need both row and column alignment → Use CSS Grid instead